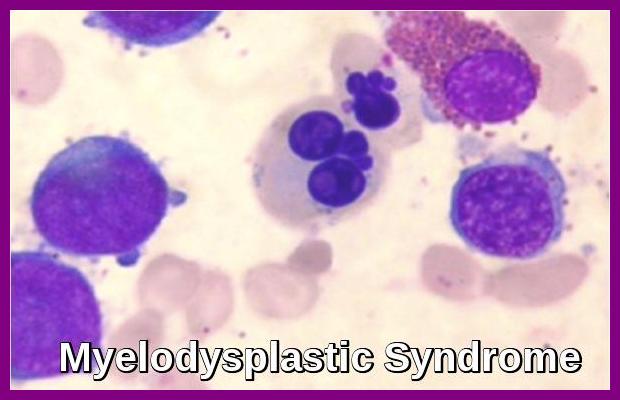
Myelodysplastic Syndrome Bone Marrow Findings
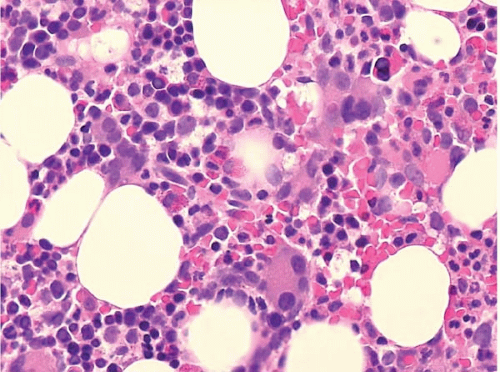
Myelodysplastic syndrome bone marrow findings. Unilineage marrow dysplasia with pancytopenia OR. Symptoms are referable to the specific cell line most affected and may include fatigue weakness pallor secondary to anemia increased infections and fever secondary to. We retrospectively analyzed a cohort of 216 MDS patients to explore the prognostic value of the percentage of mature monocyte in bone marrow.
What happens in myelodysplastic syndrome is that of those abnormal cells that are proliferating quickly are dying within the bone marrow before they get. Hematologic and cytogenetic data were collected on 401 myelodysplastic syndromes MDS patients in Japan and their clinical relevance was analyzed. The myelodysplastic syndrome MDS is group of disorders typified by peripheral cytopenia dysplastic hematopoietic progenitors a hypercellular or hypocellular bone marrow and a high risk of conversion to acute myeloid leukemia.
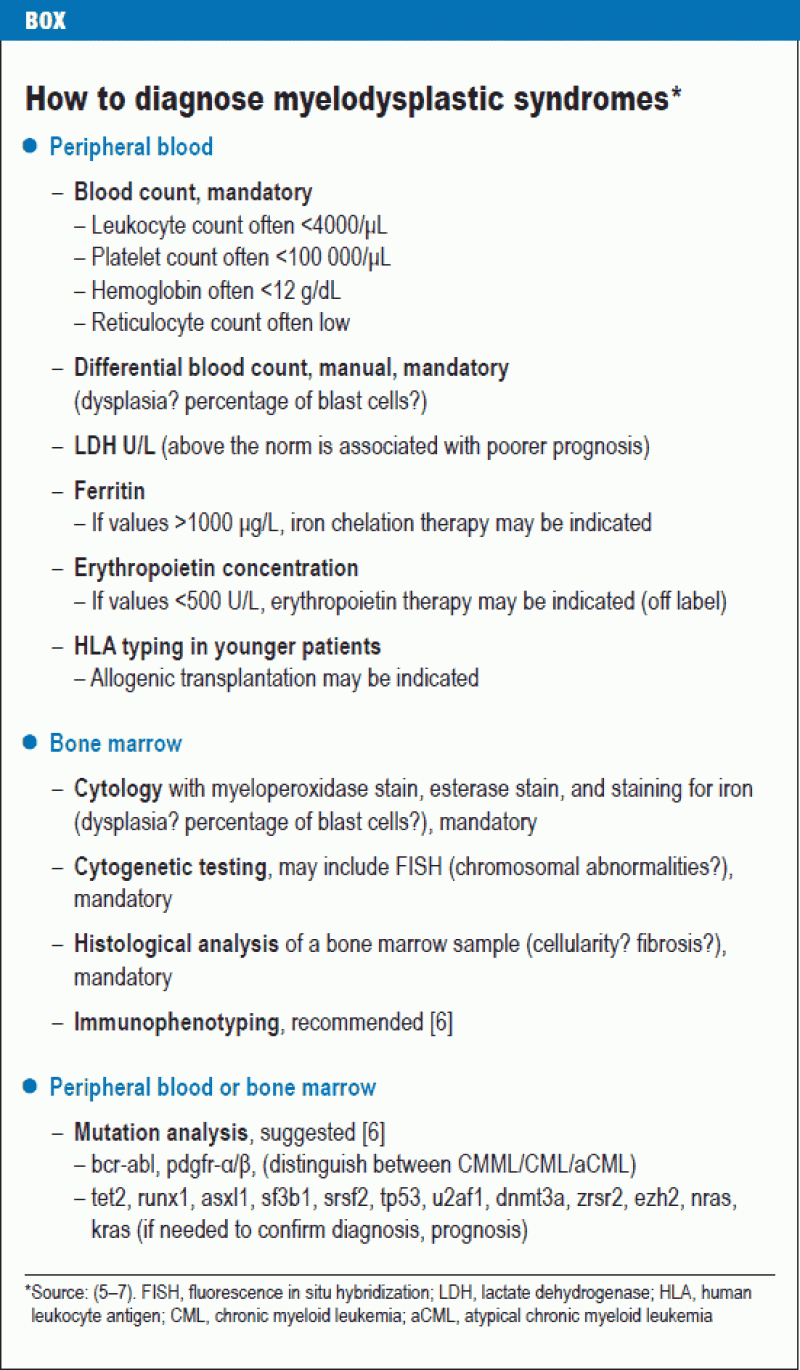
Forty bone-marrow trephine biopsies of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes MDS were studied and compared with bone marrow smears. The subtype is determined using the results of blood and bone marrow tests. Learn about these tests and how MDS is diagnosed MDS subtype is determined using either the World Health Organization WHO classification system or the French-American-British FAB classification system but the WHO classification is more commonly used today.
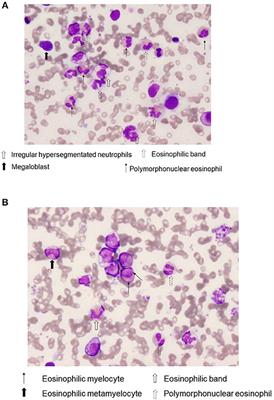
Low white blood cell levels may lead to infections. Features of abnormal erythropoiesis and myelopoiesis although different from those observed in smears were easily detectable. Platelet levels may also be low which can cause bleeding and bruising.
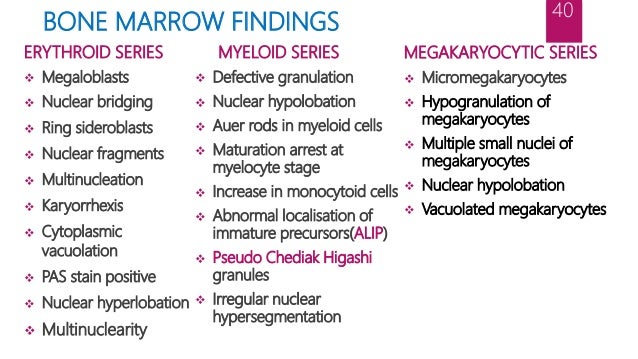
Iron stores often increased Disordered dysplastic differentiation affecting all 3 lineages Myelofibrosis in therapy related MDS. Abnormalities in this test provide the first sign of the disease. The presence of progressive cytopenias despite cellular bone marrows and dyspoiesis in one or more cell lines.
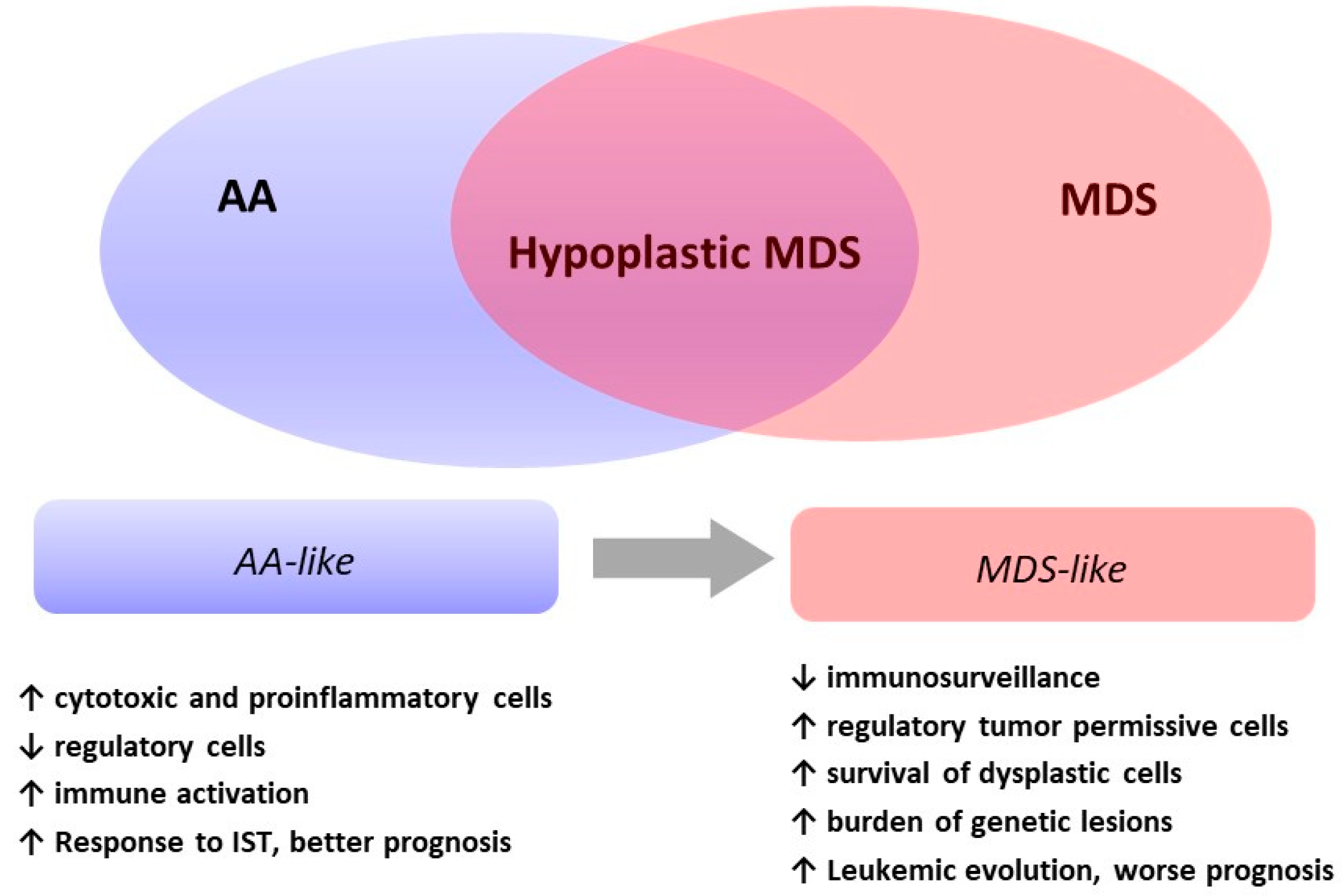
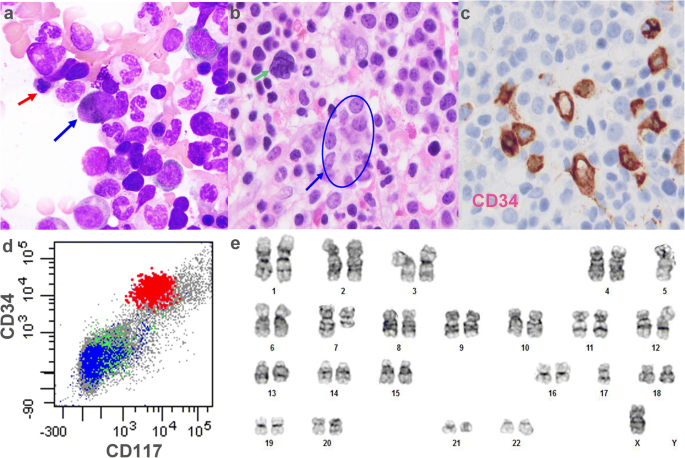
Myelodysplastic syndromes MDS is a group of heterogeneous myeloid clonal diseases originating from hematopoietic stem cells. The myelodysplastic syndrome MDS is group of disorders typified by peripheral cytopenia dysplastic hematopoietic progenitors a hypercellular or hypocellular bone marrow and a high risk of conversion to acute myeloid leukemia. It proved possible to make the diagnosis of MDS on the basis of bone-marrow biopsies.
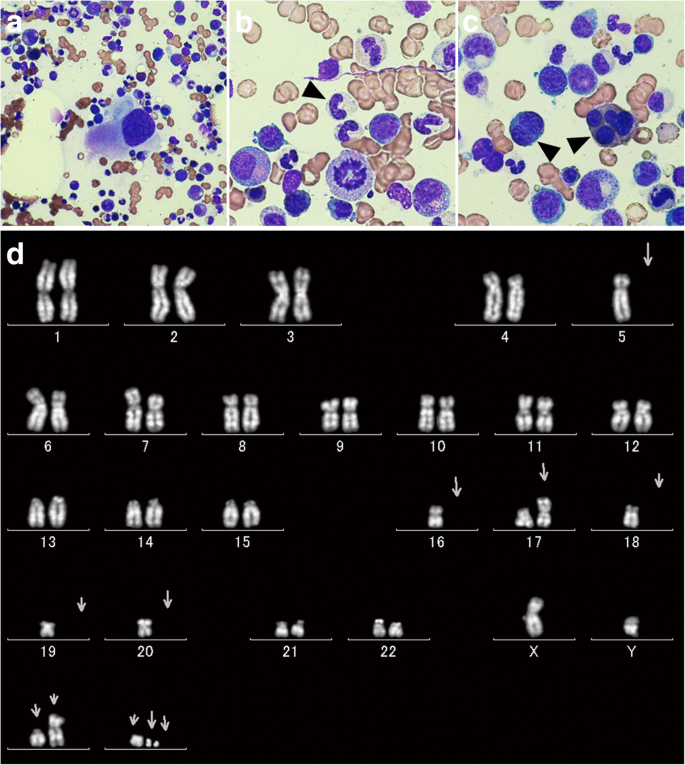
. More than 50 of the MDS patients with hypocellular bone marrow had 5 marrow blasts at the time of MDS diagnosis and frequently had complex aberrations chromosome changes at three or more regions.
Forty bone-marrow trephine biopsies of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes MDS were studied and compared with bone marrow smears.
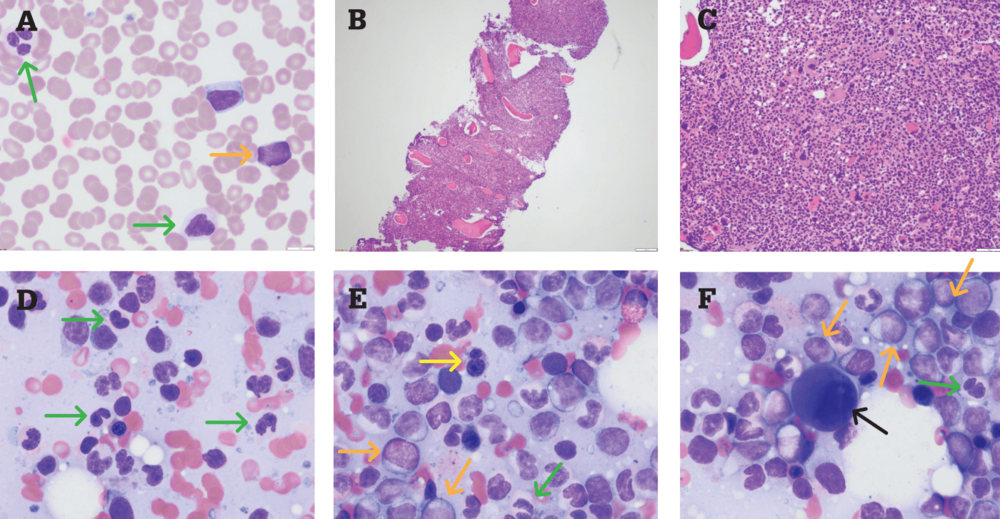
We retrospectively analyzed a cohort of 216 MDS patients to explore the prognostic value of the percentage of mature monocyte in bone marrow. Platelet levels may also be low which can cause bleeding and bruising. More than 50 of the MDS patients with hypocellular bone marrow had 5 marrow blasts at the time of MDS diagnosis and frequently had complex aberrations chromosome changes at three or more regions. Persistent cytopenia s with any of the following. Myelodysplastic syndromes MDS are a heterogeneous group of clonal hematological conditions affecting the hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow associated with ineffective hematopoiesis and manifesting as peripheral cytopenias and morphologic dysplasia in hematopoietic elements with less than 20 blasts in blood or bone marrow. Low white blood cell levels may lead to infections. Two morphologic findings are common to all types of MDS however. Myelodysplastic syndromes MDS is a group of heterogeneous myeloid clonal diseases originating from hematopoietic stem cells. Abnormalities in this test provide the first sign of the disease.
Symptoms are referable to the specific cell line most affected and may include fatigue weakness pallor secondary to anemia increased infections and fever secondary to. Usually hypercellular or normocellular 10 are hypocellular. More than 50 of the MDS patients with hypocellular bone marrow had 5 marrow blasts at the time of MDS diagnosis and frequently had complex aberrations chromosome changes at three or more regions. We retrospectively analyzed a cohort of 216 MDS patients to explore the prognostic value of the percentage of mature monocyte in bone marrow. Iron stores often increased Disordered dysplastic differentiation affecting all 3 lineages Myelofibrosis in therapy related MDS. Several cylindrical confronting cisternae CCC were present in macrophages and an endothelial cell. Clinically elevated mature monocyte in bone marrow is often observed but its clinical value still remains unclear.


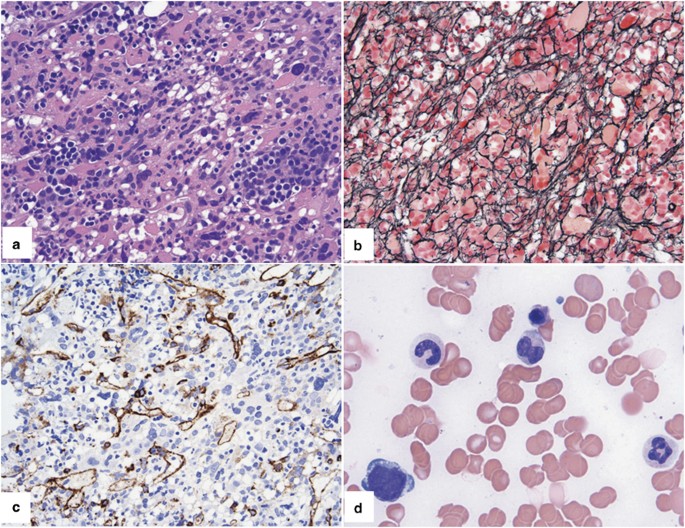




/myelodysplastic-syndrome-rcmd-[1-bm072-1].jpeg?Width=600&Height=450&Format=4)

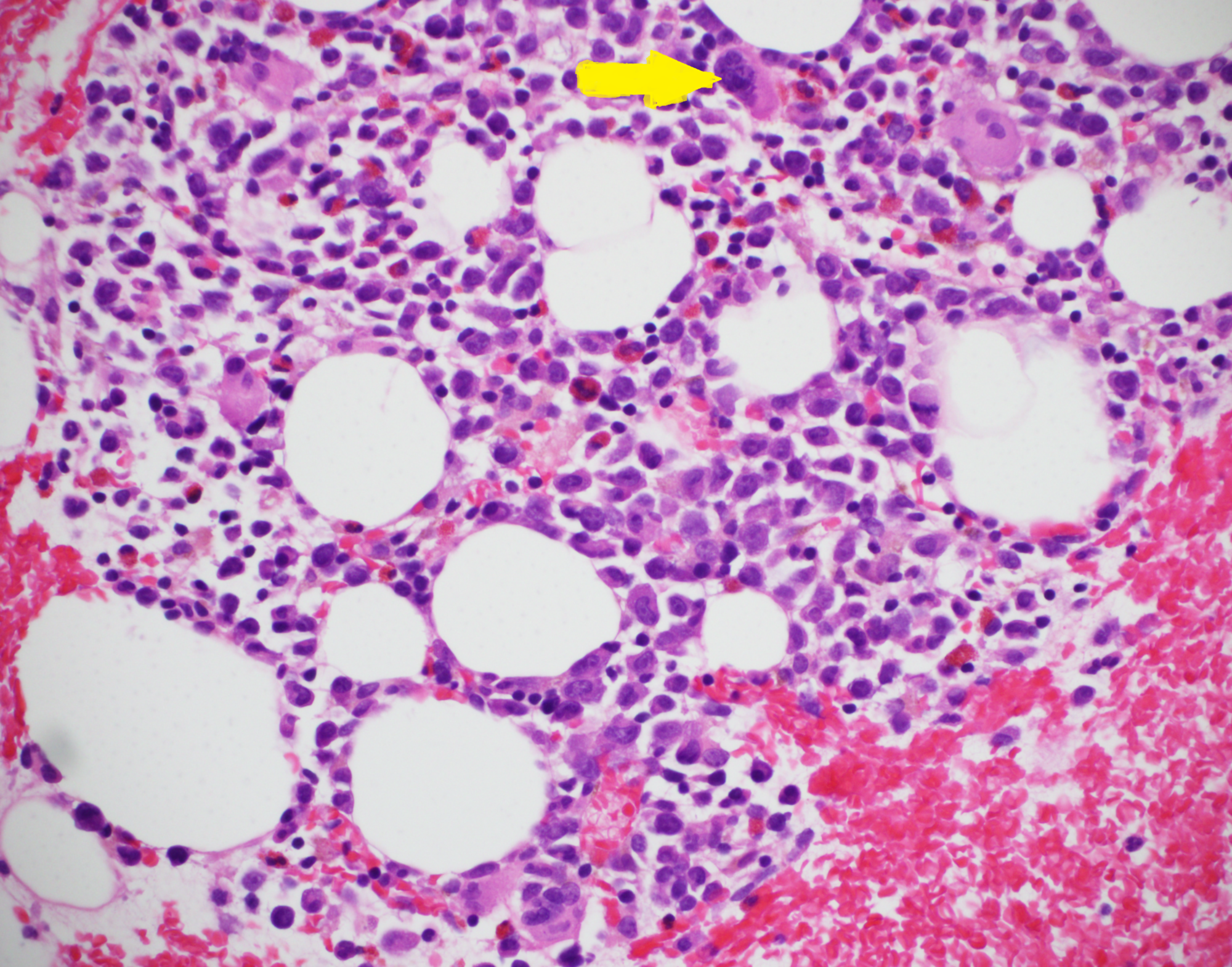


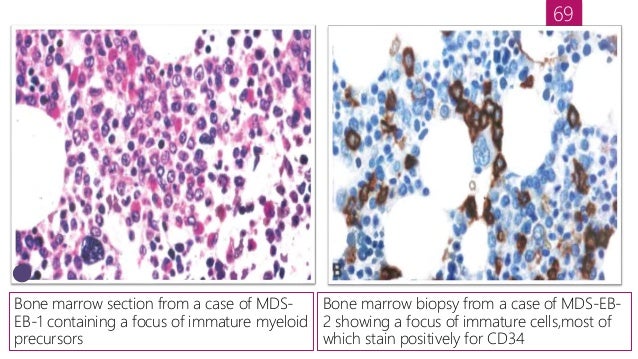


/myelodysplastic-syndrome-refractory-anemia-[1-bm00.jpeg?Width=600&Height=450&Format=4)
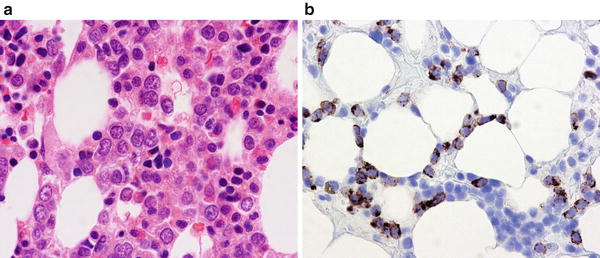

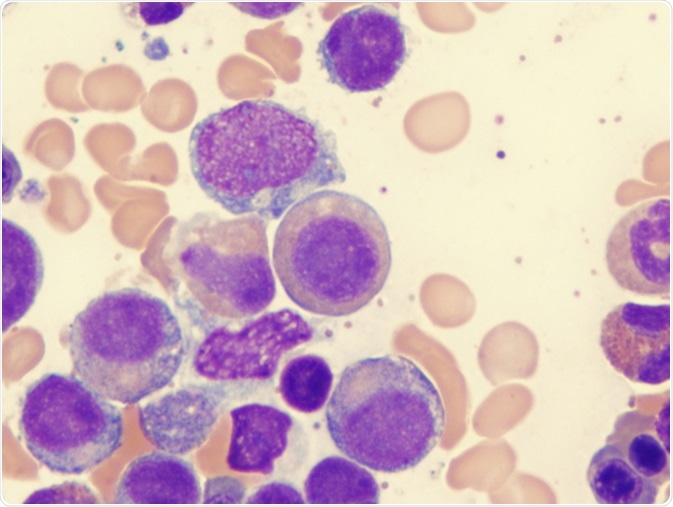

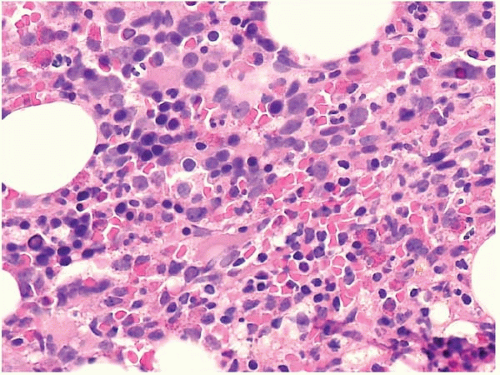








Post a Comment for "Myelodysplastic Syndrome Bone Marrow Findings"